Electrorheological fluids: structures and mechanisms
Abstract
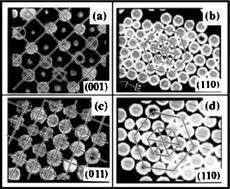
Electrorheology denotes the control of a colloid's flow properties through an electric field. We delineate the basic characteristics of electrorheological (ER) fluids, and show that the use of an effective dielectric constant concept can yield quantitative predictions. In particular, the ground state structure, the structural transition that occurs under crossed electric and magnetic fields, the high-field yield stress and its variation with particle size are all in good agreement with the experiments. The recently discovered giant electrorheological effect, owing its origin to molecular dipoles, is described and contrasted with the conventional ER effect that arises from induced polarization effects.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...