Theoretical studies on the carcinogenic activity of diol epoxide derivatives of PAH: proton affinity and aromaticity as decisive descriptors†
Abstract
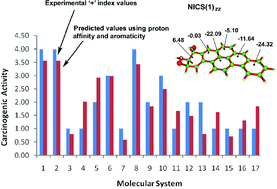
A comparative study between bay-region and nonbay-region diol epoxide (DE) derivatives of seventeen carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...