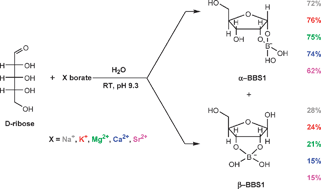
The interaction of some of the most abundant anions in seawater (borate, sulfate and carbonate/bicarbonate) with D-ribose was studied by 1H, 11B and 13C NMR spectroscopy. The results confirmed that only borate improves the stability of D-ribose and favours significant amounts of the ribofuranose isomer, which is the form occurring in present day living organisms. The effect of cations (Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+ and Sr2+) on ribose–borate-bound species was also studied, and it was found that the divalent cations induce a small increase in the relative amounts of ribopyranose isomers in solution and a corresponding decrease in the abundance of the ribofuranose isomers. It was also found that the stability of ribose–borate-bound species, when compared with free ribose over a wide range of temperature and pH values, is higher for compounds with borate, which are stable even at a relatively low pH (6.6) and a relatively high temperature (60 °C).
The stability of ribose under moderate pH and relatively high temperature conditions, in the presence of species that occur in seawater, is important for the viability of the early synthetic steps that led to the first nucleotides, which predated the formation of more complex structures, such as RNA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...