Flow-induced thermal effects on spatial DNA melting
Abstract
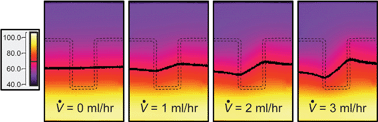
Continuous-flow temperature gradient microfluidics can be used to perform spatial DNA melting analysis. To accurately characterize the melting behavior of PCR amplicon across a spatial temperature gradient, the temperature distribution along the microfluidic channel must be both stable and known. Although temperature change created by micro-flows is often neglected, flow-induced effects can cause significant local variations in the temperature profile within the fluid and the closely surrounding substrate. In this study, microfluidic flow within a substrate with a quasi-linear temperature gradient has been examined experimentally and numerically. Serpentine geometries consisting of 10 mm long channel sections joined with 90° and/or 180° bends were studied. Infrared thermometry was used to characterize the surface temperature variations and a 3-D conjugate heat transfer model was used to predict interior temperatures for multiple device configurations. The thermal interaction between adjacent counter-flow channel sections, which is related to their spacing and substrate material properties, contributes significantly to the temperature profile within the microchannel and substrate. The volumetric flow rate and axial temperature gradient are directly proportional to the thermal variations within the device, while these flow-induced effects are largely independent of the cross-sectional area of the microchannel. The quantitative results and qualitative trends that are presented in this study are applicable to temperature gradient heating systems as well as other microfluidic thermal systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...