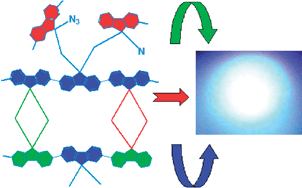
High quality white light generation with high colour rendering index (CRI) was achieved by integrating a cross-linkable azide functionalized polyfluorene derivative, namely poly[(9,9-dihexylfluorene)-co-alt-(9,9-bis(6-azidohexyl)fluorene)] (PFA), as a down-converting fluorescent material on the inorganic n-UV InGaN/GaN LED platform. For comparison, two other polyfluorene based polymers, namely poly[(9,9-dihexylfluorene)-co-alt-(9,9-bis(6-bromohexyl)fluorene)] (PFB) and poly[9,9-dihexyl-9H-fluorene] (PF), were tested for white light generation. While PFA and PF both led to white light generation, PFB fell out of the white region on the chromaticity diagram. Compared to PFA, both of the control groups (PF and PFB) exhibited much lower CRI. To gain a better insight into the mechanisms playing a key role for the generation of such high quality white light in PFA, all of these polymers were further subjected to a series of experiments such as controlled exposure to heat at 220 °C for 2 h under Ar and in air. The polymers PFA and PFB, which include cross-linkable groups, produced broad emission spectra in the region of 430–650 nm upon annealing in the absence of oxygen under Ar atmosphere while almost no change was observed in the emission spectrum of PF without any cross-linkable groups. PFA undergoes cross-linking through the decomposition of azide leading to reactive nitrene species, whereas in PFB cross-linking probably occurs viadebromination. This result clearly proved that the broadening can not be attributed only to photo or thermal oxidation, but it is also due to cross-linking. PFA was also exposed to n-UV light from the InGaN/GaN LED to investigate its photostability. In these experiments, the spectral changes in absorbance and emission properties and thermal transitions of these polymers were monitored by FT-IR, UV-Vis and fluorescent spectrometry, and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). These experiments indicated that PFA provides high quality white light opportunely via cross-linking and remains stable once cross-linking is formed in a solid film.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...