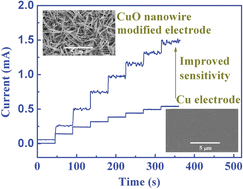
An improved sensitivity non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on a CuO nanowire modified Cu electrode†
Abstract
CuO
- This article is part of the themed collection: 150th Anniversary Collection: Highly Cited Articles
* Corresponding authors
a
College of Chemical Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, P. R. China
E-mail:
xiaodan@scu.edu.cn
Fax: +86 28 8540 7859
Tel: +86 28 8540 7958
b College of Life Sciences, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, P. R. China
c
Department of Chemistry, Hong Kong Baptist University, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong SAR, P.R. China
E-mail:
mfchoi@hkbu.edu.hk
Fax: +852 3411 7348
Tel: +852 3411 7839
CuO

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Z. Zhuang, X. Su, H. Yuan, Q. Sun, D. Xiao and M. M. F. Choi, Analyst, 2008, 133, 126 DOI: 10.1039/B712970J
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
