Abstract
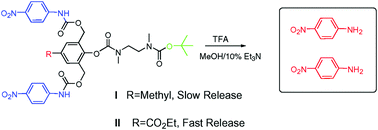
Self-immolative dendrimers are tree-like platforms, which can spontaneously release all their end-group molecules through a single activation event at the dendrimer’s focal point. This triggering event induces domino-like fragmentations, which leads to complete disassembly of the dendrimer into its separate building blocks. In this report, we demonstrate a simple approach to control the disassembly-rate of self-immolative dendrimers. Two types of dendrons were synthesized. One with a
- This article is part of the themed collection: Dendrimers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...