Combined similarity and QSPR virtual screening for guest molecules of β-cyclodextrin†
Abstract
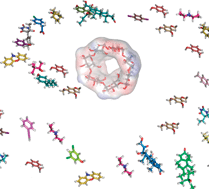
We describe a similarity-based screening approach combined with a quantitative prediction of affinity based on physicochemical descriptors, for the efficient identification of new, high affinity

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...