Novel N-(3-carboxyl-9-benzylcarboline-1-yl)ethylamino acids: synthesis, anti-proliferation activity and two-step-course of intercalation with calf thymus DNA†
Abstract
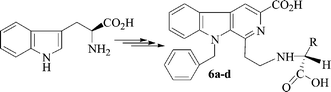
To explore the intercalating mechanism of β-carbolines, four novel N-(3-carboxyl-9-benzylcarboline-1-yl)ethylamino acids [-phenylalanine (6a), -alanine (6b), -isoleucine (6c) and -glycine (6d)] were prepared here. Their in vitro anticancer activities were examined by their anti-proliferation for 5 human carcinoma cell lines. The average IC50s against 5 human carcinoma cell lines are 53.54 µM, 118.77 µM, 147.34 µM and greater than 291.63 µM for 6a, 6b, 6c and 6d, respectively. The DNA intercalating mechanism of 6a–d was approved by the comparison of the parameters and signals of UV,

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...