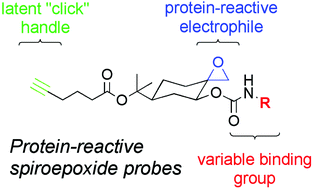
We recently reported the pharmacological screening of a natural products-inspired library of spiroepoxide probes, resulting in the discovery of an agent MJE3 that displayed anti-proliferative effects in human breast cancer cells. MJE3 was found to covalently inactivate phosphoglycerate mutase-1 (PGAM1), a glycolytic enzyme with postulated roles in cancer cell metabolism and proliferation. Considering that MJE3 is one of the first examples of a cell-permeable, small-molecule inhibitor for PGAM1, we pursued a detailed examination of its mechanism and structural requirements for covalent inactivation. MJE3 was found to label PGAM1 on lysine-100, a conserved active site residue implicated in substrate recognition. Structural features of MJE3 important for PGAM1 labeling included two key recognition elements (an indole ring and carboxylic acid), the stereochemical orientation of the spiroepoxide, and presentation of these various binding/reactive groups on a rigid cyclohexane scaffold. Modeling studies of the docked MJE3–PGAM1 complex provide a structural rationale for these stringent requirements. Overall, these studies indicate that a special combination of binding and reactive elements are united in the MJE3 structure to inactivate PGAM1. More generally, our findings provide further evidence that useful pharmacological tools can emerge from screening structurally diverse libraries of protein-reactive probes.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...