Cell detection and counting through cell lysate impedance spectroscopy in microfluidic devices†
Abstract
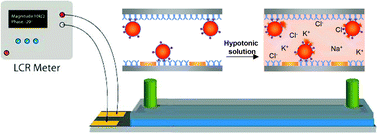
Cell-based microfluidic devices have attracted interest for a wide range of applications. While optical cell counting and flow cytometry-type devices have been reported extensively, sensitive and efficient non-optical methods to detect and quantify cells attached over large surface areas within microdevices are generally lacking. We describe an electrical method for counting cells based on the measurement of changes in conductivity of the surrounding medium due to ions released from surface-immobilized cells within a microfluidic channel. Immobilized cells are lysed using a low conductivity, hypotonic media and the resulting change in impedance is measured using surface patterned electrodes to detect and quantify the number of cells. We found that the bulk solution conductance increases linearly with the number of isolated cells contributing to solution ion concentration. The method of cell lysate impedance spectroscopy is sensitive enough to detect 20 cells µL–1, and offers a simple and efficient method for detecting and enumerating cells within microfluidic devices for many applications including measurement of CD4 cell counts in HIV patients in resource-limited settings. To our knowledge, this is the most sensitive approach using non-optical setups to enumerate immobilized cells. The microfluidic device, capable of isolating specific cell types from a complex bio-fluidic and quantifying cell number, can serve as a single use cartridge for a hand-held instrument to provide simple, fast and affordable cell counting in point-of-care settings.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...