Microfabrication-based modulation of embryonic stem cell differentiation
Abstract
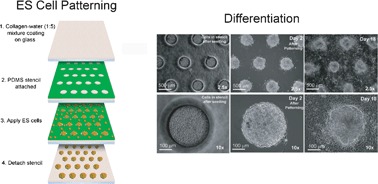
Embryonic stem (ES) cells form spontaneous aggregates during differentiation, and cell–cell communication in the aggregates plays an important role in differentiation. The development of a controlled differentiation scheme for ES cells has been hindered by the lack of a reliable method to produce uniform aggregate sizes. Conventional techniques, such as hanging drop and suspension cultures, do not allow precise control over size of ES cell aggregates. To surmount this problem, we microfabricated adhesive stencils to make mouse ES (mES) cell aggregates of specific sizes ranging from 100 µm to 500 µm in diameter. With this technique, we studied the effect of the initial aggregate size on ES cell differentiation. After 20 days of induction of differentiation, we analyzed the stem cell populations using gene and protein expression assays as well as biochemical functions. Notably, we found that germ layer differentiation depends on the initial size of the ES cell aggregate. Among the ES cell aggregate sizes tested, the aggregates with 300 µm diameter showed similar differentiation profiles of three germ layers as embryoid bodies made using the “hanging drop” technique. The smaller (100 µm) aggregates showed the increased expression of ectodermal markers compared to the larger (500 µm) aggregates, while the 500 µm aggregates showed the increased expression of mesodermal and endodermal markers compared to the 100 µm aggregates. These results indicate that the initial size of the aggregate is an important factor for ES cell differentiation, and can affect germ layer selection as well as the extent of differentiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...