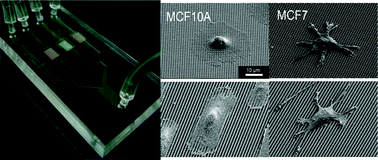
A label-free microfluidic method for separation and enrichment of human breast cancer cells is presented using cell adhesion as a physical marker. To maximize the adhesion difference between normal epithelial and cancer cells, flat or nanostructured polymer surfaces (400 nm pillars, 400 nm perpendicular, or 400 nm parallel lines) were constructed on the bottom of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microfluidic channels in a parallel fashion using a UV-assisted capillary moulding technique. The adhesion of human breast epithelial cells (MCF10A) and cancer cells (MCF7) on each channel was independently measured based on detachment assays where the adherent cells were counted with increasing flow rate after a pre-culture for a period of time (e.g., one, two, and four hours). It was found that MCF10A cells showed higher adhesion than MCF7 cells regardless of culture time and surface nanotopography at all flow rates, resulting in label-free separation and enrichment of cancer cells. For the cell types used in our study, an optimum separation was found for 2 hours pre-culture on the 400 nm perpendicular line pattern followed by flow-induced detachment at a flow rate of 200 µl min−1. The fraction of MCF7 cells was increased from 0.36 ± 0.04 to 0.83 ± 0.04 under these optimized conditions.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...