In-situ synthesis of reactive hydroxyapatite nano-crystals for a novel approach of surface grafting polymerization
Abstract
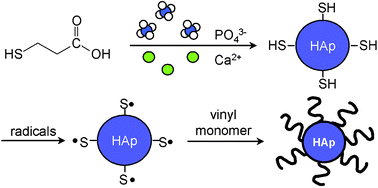
A novel approach to surface modification of hydroxyapatite (HAp) nano-crystals was described based on in-situ synthesis of surface

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...