Comparative metallomics for transgenic and non-transgenic soybeans
Abstract
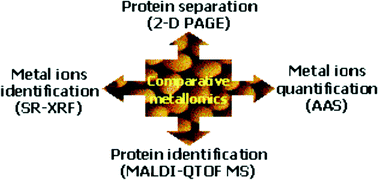
In this work, a comparative metallomics of transgenic and non-transgenic soybeans [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] was performed. Soybean proteins were extracted with a proper buffer and separated by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Metal ions bound to a set of eight proteins randomly selected (ranging from 13.98 to 54.87 kDa), were characterized by matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization quadrupole-time of flight mass spectrometry and mapped using synchrotron radiation X-ray spectrometry. The metal ions detected were: Ca(II), Cu(II), Fe(II), Mn(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II). Transgenic and non-transgenic soybeans proteins were found to display typical and random profiles for metal ions binding. To test the reliability of the qualitative metal ions profiles, quantification of Ca(II), Cu(II) and Fe(II) was performed via microwave-assisted decomposition in mini-vials followed by atomic absorption spectrometry determination. Qualitative and quantitative metallomics was found to be coherent and to match profiles expected from the known protein functions. The protein of spot 5, with molar mass of 37.62 kDa (amino acid sequence presented), was found to display the most characteristic change in metal ions content, with higher Ca(II), Cu(II) and Fe(II) concentrations for transgenic soybeans.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...