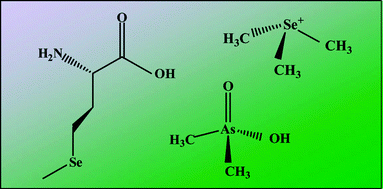
A procedure for the simultaneous determination of six selenium species and six arsenic species in human urine by ion-pair, reversed-phase liquid chromatography coupled to ICP-MS has been developed. Selenium species, trimethylselenonium ion (TMSe), selenocystine (SeCys), selenite (SeIV), selenourea (SeUr), selenomethionine (SeMet), selenoethionine (SeEt), and arsenic species, arsenocholine (AsC), arsenobetaine (AsB), dimethylarsinic acid (DMA), methylarsonic acid (MMA), arsenite (AsIII), arsenate (AsV) were separated on a C8 reversed phase column by a mobile phase of 13.0 mmol l−1 tetrabutylammonium hydroxide (ion-pair reagent) and 1.3% methanol at pH 5.7–5.8 (adjusted with malonic acid). The total analysis took less than 10 min with isocratic elution at a flow rate of 1.0 ml min−1, and was free from chloride interference due to the complete separation of the analyte species from chloride. The detection limits, in synthetic urine for an injection volume of 50 μL, ranged between 0.1 and 0.4 μg l−1 for the six arsenic species (except AsC) and between 0.7 and 2 μg l−1 for the six selenium species (at m/z 78). The repeatability was less than 10% (RSD) for 1 μg l−1 arsenic species and 5 μg l−1 selenium species, except for AsC. Quantification was based on response factors in a synthetic urine matrix relative that of AsV in the mobile phase. The response factors for selenium species showed considerable compound dependence. Recoveries from spiked urine samples ranged from 81% to 103%, except for SeUr and SeEt, which were not recovered. The method was applied to the determination of arsenic and selenium species in urine, which only required filtering through a 0.45 μm membrane filter and dilution with mobile phase in order to measure arsenic and selenium urinary metabolites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...