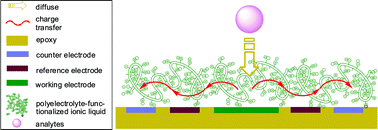
As a green process, electrochemistry in aqueous solution without a supporting electrolyte has been described based on a simple polyelectrolyte-functionalized ionic liquid (PFIL)-modified electrode. The studied PFIL material combines features of ionic liquids and traditional polyelectrolytes. The ionic liquid part provides a high ionic conductivity and affinity to many different compounds. The polyelectrolyte part has a good stability in aqueous solution and a capability of being immobilized on different substrates. The electrochemical properties of such a PFIL-modified electrode assembly in a supporting electrolyte-free solution have been investigated by using an electrically neutral electroactive species, hydroquinone (HQ) as the model compound. The partition coefficient and diffusion coefficient of HQ in the PFIL film were calculated to be 0.346 and 4.74 × 10−6 cm2 s−1, respectively. Electrochemistry in PFIL is similar to electrochemistry in a solution of traditional supporting electrolytes, except that the electrochemical reaction takes place in a thin film on the surface of the electrode. PFILs are easily immobilized on solid substrates, are inexpensive and electrochemically stable. A PFIL-modified electrode assembly is successfully used in the flow analysis of HQ by amperometric detection in solution without a supporting electrolyte. The results indicate a green electrochemical methodology in supporting electrolyte-free solution and a potential application in amperometric detection in a flow system without any supporting electrolyte in the solution, such as the high performance liquid chromatography electrochemical detection (HPLC-ECD) system.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...