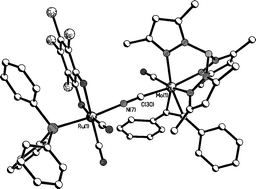
Two series of stable cyanide-bridged linkage isomers, namely [(o-O2C6Cl4)(Ph3P)(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)MnL(NO)(η-C5Me5)] (XY = CN or NC, L = CNBut or CNXyl) and [(o-O2C6Cl4)L(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)M(CO)(PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′] {M = Mo or W, L = PPh3 or P(OPh)3, Tp′ = hydrotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate} have been synthesised; pairs of isomers are distinguishable by IR spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry. The molecular structure of [(o-O2C6Cl4)(Ph3P)(OC)2Ru(µ-NC)Mo(CO)(PhC
CPh)Tp′] {M = Mo or W, L = PPh3 or P(OPh)3, Tp′ = hydrotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate} have been synthesised; pairs of isomers are distinguishable by IR spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry. The molecular structure of [(o-O2C6Cl4)(Ph3P)(OC)2Ru(µ-NC)Mo(CO)(PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′] has the catecholate-bound ruthenium atom cyanide-bridged to a Mo(CO)(PhC
CPh)Tp′] has the catecholate-bound ruthenium atom cyanide-bridged to a Mo(CO)(PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′ unit in which the alkyne acts as a four-electron donor; the alignment of the alkyne relative to the Mo–CO vector suggests the fragment (CN)Ru(CO)2(PPh3)(o-O2C6Cl4) acts as a π-acceptor ligand. The complexes [(o-O2C6Cl4)(Ph3P)(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)Mn(NO)L(η-C5Me5)] undergo three sequential one-electron oxidation processes with the first and third assigned to oxidation of the ruthenium-bound o-O2C6Cl4 ligand; the second corresponds to oxidation of Mn(I) to Mn(II). The complexes [(o-O2C6Cl4)L(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)M(CO)(PhC
CPh)Tp′ unit in which the alkyne acts as a four-electron donor; the alignment of the alkyne relative to the Mo–CO vector suggests the fragment (CN)Ru(CO)2(PPh3)(o-O2C6Cl4) acts as a π-acceptor ligand. The complexes [(o-O2C6Cl4)(Ph3P)(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)Mn(NO)L(η-C5Me5)] undergo three sequential one-electron oxidation processes with the first and third assigned to oxidation of the ruthenium-bound o-O2C6Cl4 ligand; the second corresponds to oxidation of Mn(I) to Mn(II). The complexes [(o-O2C6Cl4)L(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)M(CO)(PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′] are also first oxidised at the catecholate ligand; the second oxidation, and one-electron reduction, are based on the M(CO)(PhC
CPh)Tp′] are also first oxidised at the catecholate ligand; the second oxidation, and one-electron reduction, are based on the M(CO)(PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′ fragment. Chemical oxidation of [(o-O2C6Cl4)(Ph3P)(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)MnL(NO)(η-C5Me5)] with [Fe(η-C5H4COMe)(η-C5H5)][BF4], or of [(o-O2C6Cl4)L(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)M(CO)(PhC
CPh)Tp′ fragment. Chemical oxidation of [(o-O2C6Cl4)(Ph3P)(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)MnL(NO)(η-C5Me5)] with [Fe(η-C5H4COMe)(η-C5H5)][BF4], or of [(o-O2C6Cl4)L(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)M(CO)(PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′] with AgBF4, gave the paramagnetic monocations [(o-O2C6Cl4)(Ph3P)(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)MnL(NO)(η-C5Me5)]+ and [(o-O2C6Cl4)L(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)M(CO)(PhC
CPh)Tp′] with AgBF4, gave the paramagnetic monocations [(o-O2C6Cl4)(Ph3P)(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)MnL(NO)(η-C5Me5)]+ and [(o-O2C6Cl4)L(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)M(CO)(PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′]+, the ESR spectra of which are consistent with ruthenium-bound semiquinone ligands. Linkage isomers are distinguishable by the magnitude of the 31P hyperfine coupling constant; complexes with N-bound Ru(o-O2C6Cl4) units also show small hyperfine coupling to the nitrogen atom of the cyanide bridge.
CPh)Tp′]+, the ESR spectra of which are consistent with ruthenium-bound semiquinone ligands. Linkage isomers are distinguishable by the magnitude of the 31P hyperfine coupling constant; complexes with N-bound Ru(o-O2C6Cl4) units also show small hyperfine coupling to the nitrogen atom of the cyanide bridge.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′] {M = Mo or W, L = PPh3 or P(OPh)3, Tp′ = hydrotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate} have been synthesised; pairs of isomers are distinguishable by
CPh)Tp′] {M = Mo or W, L = PPh3 or P(OPh)3, Tp′ = hydrotris(3,5-dimethylpyrazolyl)borate} have been synthesised; pairs of isomers are distinguishable by ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′] has the catecholate-bound ruthenium atom cyanide-bridged to a Mo(CO)(PhC
CPh)Tp′] has the catecholate-bound ruthenium atom cyanide-bridged to a Mo(CO)(PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′ unit in which the
CPh)Tp′ unit in which the ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′] are also first oxidised at the catecholate
CPh)Tp′] are also first oxidised at the catecholate ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′ fragment. Chemical
CPh)Tp′ fragment. Chemical ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′] with AgBF4, gave the paramagnetic monocations [(o-O2C6Cl4)(Ph3P)(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)MnL(NO)(η-C5Me5)]+ and [(o-O2C6Cl4)L(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)M(CO)(PhC
CPh)Tp′] with AgBF4, gave the paramagnetic monocations [(o-O2C6Cl4)(Ph3P)(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)MnL(NO)(η-C5Me5)]+ and [(o-O2C6Cl4)L(OC)2Ru(µ-XY)M(CO)(PhC![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) CPh)Tp′]+, the ESR spectra of which are consistent with ruthenium-bound
CPh)Tp′]+, the ESR spectra of which are consistent with ruthenium-bound 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...