Contact angle determination of nanoparticles: film balance and scanning angle reflectometry studies
Abstract
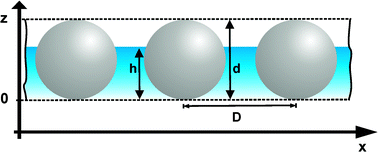
Stöber silica nanoparticles of diameter about 45, 60 and 100 nm and different hydrophobicity are used to produce monolayers at a water–air interface. Both the surface pressure–area isotherms and the reflectivity angle of incidence curves of the layers have been measured in a Wilhelmy film balance. The contact angle of the as-prepared particles have been determined from the isotherms by two different evaluation methods, and compared to those obtained from in situ scanning angle reflectometry (SAR) measurements. SAR is proved to be an effective tool for the estimation of contact angles on nanoparticles of different wettability, using a modified version of the previously published gradient layer model (E. Hild, T. Seszták, D. Völgyes and Z. Hórvölgyi, Prog. Colloid Polym. Sci., 2004, 125, 61, ref. 1) for evaluation. The results are in fairly good agreement with those determined from the non-dissipative part of the isotherms of the as prepared particles, assuming a weakly cohesive film model (S. Bordács, A. Agod and Z. Hórvölgyi, Langmuir, 2006, 22, 6944, ref. 2). It seems that the traditional way to calculate the contact angle from the film balance experiments (J.H. Clint and N. Quirke, Colloids Surf., A, 1993, 78, 277, ref. 3) results in unreasonably high contact angles for the investigated systems and the homogeneous layer optical model gives unrealistic film thickness values in the case of hydrophobic particles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...