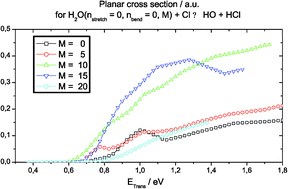
The first four dimensional (4D) quantum scattering calculations on the tetra-atomic H2O + Cl ↔ HO + HCl reactions are reported. With respect to a full (6D) treatment, only the planar constraint and a fixed length for the HO spectator bond are imposed. This work explicitly accounts for the bending and local HO stretching vibrations in H2O, for the vibration of HCl and for the in-plane rotation of the H2O, HO and HCl molecules. The calculations are performed with the potential energy surface of Clary et al. and use a Born–Oppenheimer type separation between the motions of the light and the heavy nuclei. State-to-state cross sections are reported for a collision energy range 0–1.8 eV measured with respect to H2O + Cl. For the H2O + Cl reaction, present results agree with previous (3D) non planar calculations and confirm that excitation of the H2O stretching promotes more reactivity than excitation of the bending. New results are related to the rotation of the H2O molecule: the cross sections are maximal for planar rotational states corresponding to 10 < M < 15, independently of the H2O initial vibrational state. At low collision energy (<0.8 eV), product state analysis reveals wider rotational distributions for the HCl than for the OH products. For the HO + HCl reaction, the rotational excitation of the HO and HCl reactants does not significantly promote reaction. The water molecules are essentially formed in the fundamental, first bending and local stretching vibrational states.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...