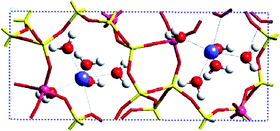
Computational methods are described that model accurately the structure of hydrated Ca-bearing zeolites. Using Goosecreekite as a model system we probe the influence of framework ordering, cation siting and hydration of pores on the structure and its stability. We develop a methodology which allows the location of Al within the framework to be determined together with the position of extra-framework cations, in a stepwise fashion, progressing from an anhydrous model, via a dielectric continuum model, to finally, a fully atomistic model of the water in the intrazeolite pore space. Our methods reveal the complex interplay of short- and long-range interactions on the optimal structure of such materials.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...