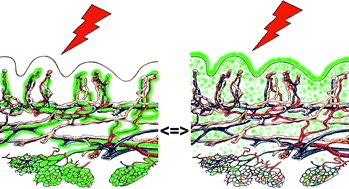
In photodynamic therapy (PDT) the photosensitiser 5-aminolaevulinic acid (ALA) can be used by systemic or topical application. Previous experiments showed that the photodynamic effects might not be mediated solely by porphyrins localized in the parenchyma, but also by porphyrins in the microvasculature. Therefore, the microcirculatory effects of PDT following systemic versus topical application of ALA have been investigated. Amelanotic melanomas were implanted in the dorsal skin fold chamber of Syrian Golden hamsters. ALA was injected i.v. for systemic PDT before irradiation, whereas ALA was applied to the chambers for topical PDT before irradiation with an incoherent lamp. FITC-labelled erythrocytes were injected to determine red blood cell velocity (RBCV) and functional vessel density (FVD). Twenty-four hours after PDT tissue was taken for histology and immunohistochemistry to reveal the degree of apoptosis and to show the accumulation of leukocytes. FVD or RBCV was not altered significantly by systemic or topical low-dose PDT (10 J cm−2), whereas a significant reduction of RBCV and FVD was detected after high-dose PDT (100 J cm−2) following systemic or topical application of ALA. Systemic PDT with 100 J cm−2 stopped the flow only in the tumor center, whereas topical PDT with 100 J cm−2 lead to a breakdown of RBCV in all chamber areas. Two hours and 24 h after systemic high-dose PDT, perfused microvessels and capillaries could be detected in normal tissue and tumor periphery, in contrast to topical high-dose PDT leading to a shut down of FVD 24 h after irradiation in all areas of the chamber tissue. Histological staining revealed a more pronounced intracellular oedema and swelling of cells after topical high-dose PDT than systemic high-dose PDT. These results indicate that topical high-dose PDT with ALA has a more pronounced effect on microcirculation as compared to systemic high-dose PDT in this model.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...