Surface functionalisation of detonation diamond suitable for biological applications†
Abstract
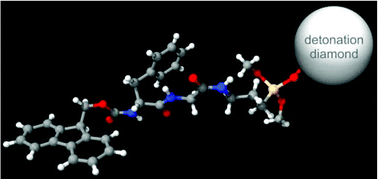
Detonation diamond is a promising material for biological applications due to its biocompatibility and fluorescence from lattice defects. Here we report on the organic functionalisation method for small detonation diamond agglomerates. After surface
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...