Copper phosphide or arsenide complexes, [Cu(EPh2)(neo)] (E = P, As, neo = 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline; trivial name: neocuprine) react selectively with the N-protected brominated serine derivatives, 2-(S)-(alkoxycarbonylamino)-3-bromomethylpropionates 1a–c (ROCOSerBr, a: R = PhCH2, b: tBu, c: Me) to give the corresponding phosphanylated or arsanylated amino acids, ROCOSerPhos (3a–c: Phos = PPh2) and ZSerArs 7 (Ars = AsPh2, Z = PhCH2OCO). The dipeptide ZAlaSerPhos 3d was likewise prepared. The phosphanes 3a–d, and the arsane 7 reacted cleanly with [Rh2(µ-Cl)2(cod)2] to give the rhodium(I) complexes [RhCl(cod)(ZSerPhos)] 8, [RhCl(cod)(BocSerPhos)] 9 (Boc = tBuOCO), [RhCl(cod)(ZAlaSerPhos)] 10, and [RhCl(cod)(ZSerArs)] 11 which were characterized by X-ray diffraction studies. A common structural feature is an intramolecular (N)H⋯Cl(Rh)-hydrogen bridge which according to NMR investigations remains intact in solution. The abstraction of chloride from the coordination sphere of Rh(I) in 8 or 10 has a profound structural impact. While in 8 and 10, the ligands bind in a monodentate fashion, via the phosphorus atom only, they serve as bidentate ligands via the phosphorus centre and the peptidic C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group in [Rh(cod)(κ2-ZSerPhos)]PF612 and [Rh(cod)(κ2-ZAlaSerPhos)]PF613. This causes also the amino acid residue structures to change from α-helix type in 8 and 10 to a β-sheet type in 12 and 13. Addition of chloride to 12 and 13 fully re-establishes the structures of 8 and 10. The complexes [RhCl(cod)(ZSerPhos)] 8 and [RhCl(cod)(BocSerPhos)] 9 show good activities in homogeneously catalyzed hydrogenations of olefins while the dipeptide complex 10 is less active. Phosphane addition to 8 greatly diminishes the catalytic activity. The cationic complex [Rh(cod)(κ2-ZAlaSerPhos)]PF6 shows low activity which, however, is greatly increased by addition of one equivalent of phosphane.
O group in [Rh(cod)(κ2-ZSerPhos)]PF612 and [Rh(cod)(κ2-ZAlaSerPhos)]PF613. This causes also the amino acid residue structures to change from α-helix type in 8 and 10 to a β-sheet type in 12 and 13. Addition of chloride to 12 and 13 fully re-establishes the structures of 8 and 10. The complexes [RhCl(cod)(ZSerPhos)] 8 and [RhCl(cod)(BocSerPhos)] 9 show good activities in homogeneously catalyzed hydrogenations of olefins while the dipeptide complex 10 is less active. Phosphane addition to 8 greatly diminishes the catalytic activity. The cationic complex [Rh(cod)(κ2-ZAlaSerPhos)]PF6 shows low activity which, however, is greatly increased by addition of one equivalent of phosphane.
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O group in [Rh(cod)(κ2-ZSerPhos)]PF612 and [Rh(cod)(κ2-ZAlaSerPhos)]PF613. This causes also the amino acid residue structures to change from α-helix type in 8 and 10 to a β-sheet type in 12 and 13. Addition of chloride to 12 and 13 fully re-establishes the structures of 8 and 10. The complexes [RhCl(cod)(ZSerPhos)] 8 and [RhCl(cod)(BocSerPhos)] 9 show good activities in homogeneously catalyzed hydrogenations of
O group in [Rh(cod)(κ2-ZSerPhos)]PF612 and [Rh(cod)(κ2-ZAlaSerPhos)]PF613. This causes also the amino acid residue structures to change from α-helix type in 8 and 10 to a β-sheet type in 12 and 13. Addition of chloride to 12 and 13 fully re-establishes the structures of 8 and 10. The complexes [RhCl(cod)(ZSerPhos)] 8 and [RhCl(cod)(BocSerPhos)] 9 show good activities in homogeneously catalyzed hydrogenations of 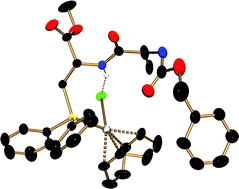

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...