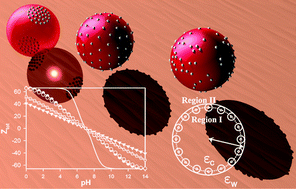
The surface site distribution and the dielectric discontinuity effects on the charging process of a spherical nanoparticle (NP) have been investigated. It is well known that electrostatic repulsion between charges on neighbouring sites tends to decrease the effective charge of a NP. The situation is more complicated close to a dielectric breakdown, since here a charged site is not only interacting with its neighbours but also with its own image charge and the image charges of all its neighbours. Coexistence of opposite charges, titration sites positions, and pH dependence are systematically studied using a grand canonical Monte Carlo method. A Tanford and Kirkwood approach has been applied to describe the interaction potentials between explicit discrete ampholytic charging sites. Homogeneous, heterogeneous and patch site distributions were considered to reproduce the titration site distribution at the solid/solution interface of natural NPs. Results show that the charging process is controlled by the balance between Coulomb interactions and the reaction field through the solid–liquid interface. They also show that the site distribution plays a crucial role in the charging process. In patch distributions, charges accumulate at the perimeter of each patch due to finite size effects. When homogeneous and heterogeneous distributions are compared, three different charging regimes are obtained. In homogeneous and heterogeneous (with quite low polydispersity indexes) distributions, the effects of the NP dielectric constant on Coulomb interactions are counterbalanced by the reaction field and in this case, the dielectric breakdown has no significant effect on the charging process. This is not the case in patch distributions, where the dielectric breakdown plays a crucial role in the charging process.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...