Impact on lipid membrane organization by free branched-chain fatty acids
Abstract
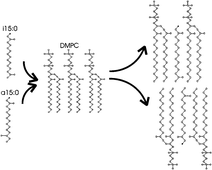
Here, we exploit the non-invasive techniques of solid-state NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) to study the effect of free iso and ante-iso branched chain fatty acids (BCFAs) on the physicochemical properties of lipid membranes. Free fatty acids are present in biological membranes at low abundance, but can influence the cellular function by modulating the membrane organization. Solid state NMR spectra of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) lipid membranes containing either free 12-methyltetradecanoic acid (a15:0) or free 13-methyltetradecanoic acid (i15:0), show significant differences in their impact on the lipid bilayer. Chain order profiles obtained by deuterium NMR on fully deuterated DMPC-d67 bilayers revealed an ordering effect induced by both fatty acids on the hydrophobic membrane core. This behavior was also visible in the corresponding DSC thermograms where the main phase transition of DMPC bilayers—indicative of the hydrophobic membrane region—was shifted to higher temperatures, with the iso isomer triggering more pronounced changes as compared to the ante-iso isomer. This is probably due to a higher packing density in the core of the lipid bilayer, which causes reduced diffusion across membranes. By utilizing the naturally occurring spin reporters nitrogen-14 and phosphorus-31 present in the hydrophilic DMPC headgroup region, even fatty acid induced changes at the membrane interface could be detected, an observation reflecting changes in the lipid headgroup dynamics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...