Computational studies of molecular hydrogen binding affinities: The role of dispersion forces, electrostatics, and orbital interactions†
Abstract
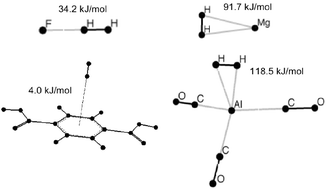
Intermolecular interactions between H2 and ligands, metals, and metal–ligand complexes determine the binding affinities of potential hydrogen storage materials (HSM), and thus their extent of potential for practical use. A brief survey of current activity on HSM is given. The key issue of binding strengths is examined from a basic perspective by surveying the distinct classes of interactions (dispersion, electrostatics, orbital interactions) in first a general way, and then in the context of calculated binding affinities for a range of model systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...