Speciation of selenocompounds by capillary HPLC coupled with ICP-MS using multi-mode gel filtration columns
Abstract
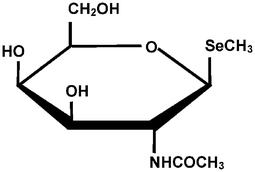
Multi-mode gel filtration HPLC columns of capillary size coupled with ICP-MS were evaluated as to the separation of naturally occurring selenocompounds. The major selenocompounds found in selenized garlic, i.e., Se-methylselenocysteine and γ-glutamyl-Se-methylselenocysteine, were separated on the narrower column (GS320A-M5D, 0.5 mm i.d. × 150 mm). The selenometabolites found in the urine of a selenium-toxicosis rat, i.e., selenosugar (1-β-methylseleno-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine) and trimethylselenonium, were also separated on the same column. On the other hand, the selenoamino acids, i.e., Se-methylselenocysteine and selenomethionine, were separated on the larger column (GS320A-M8E, 0.8 mm i.d. × 250 mm). These samples were introduced directly into the capillary columns without any pretreatment. The capillary HPLC separated these selenocompounds into distinct peaks with satisfactory sensitivity and a better S/N ratio than conventional HPLC despite that the sample volume was reduced to 1/200 (100 nl).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...