Mutagenesis of CP43-arginine-357 to serine reveals new evidence for (bi)carbonate functioning in the water oxidizing complex of Photosystem II†‡
Abstract
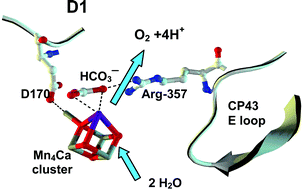
The chlorophyll-binding protein CP43 is an inner subunit of the Photosystem II (PSII) reaction center core complex of all oxygenic photoautotrophs. X-Ray structural evidence places the guanidinium cation of the conserved arginine 357 residue of CP43 within a few Ångstroms to the Mn4Ca cluster of the water-oxidizing complex (WOC) and has been implicated as a possible carbonate binding site. To test the hypothesis, the serine mutant, CP43-R357S, from Synechocystis PCC 6803 was investigated by PSII variable fluorescence (Fv/Fm) and simultaneous flash O2 yield measurements in cells and thylakoid membranes. The R357S mutant assembles PSII-WOC centers, but is unable to grow photoautotrophically. Reconstitution of O2 evolution by photoactivation and the occurrence of period-four oscillations of Fv/Fm establishes that the R357S mutant contains an assembled Mn4Ca cluster, but turnover is impaired as seen by an 11-fold larger Kok double miss parameter and faster decay of upper S states. Using pulsed light to avoid photoinactivation, wild-type cells and thylakoid membranes exhibit a 2–4-fold loss in O2 evolution rate upon partial bicarbonate depletion under multiple turnover conditions, while the R357S mutant is unaffected by bicarbonate. Arginine R357 appears to function in binding a (bi)carbonate ion essential to normal catalytic turnover of the WOC. The quantum yield of electron donation from the WOC into PSII increases with decreasing turnover rate in R357S mutant cells and involves an aborted two-flash pathway that is distinct from the classical four-flash pattern. We speculate that an altered photochemical mechanism for O2 production occurs via formation of hydrogen peroxide, by analogy to other treatments that retard the kinetics of proton release into the lumen.
- This article is part of the themed collection: In honour of James Barber

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...