Detection of single base mismatches and abasic sites using phenanthridinium as an artificial DNA base and charge donor†
Abstract
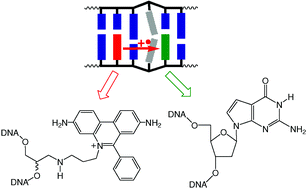
Combining the fluorescence properties of phenanthridinium as an artificial DNA base together with DNA-mediated charge transfer processes allows the homogeneous detection of DNA base mismatches and abasic sites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...