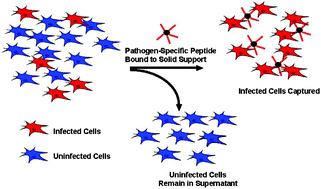
An important goal in medicine is the development of methods for cell-specific targeting of therapeutic molecules to pathogens or pathogen-infected cells. However, little progress has been made in cell-specific targeting of bacterially infected cells. Using a phage display approach, we have isolated a 20-mer peptide that binds to Mycoplasma arginini infected pancreatic β-cells in tissue culture. This peptide binds to M. arginini infected β-cells 200 times better than a control phage and is specific for the infected cells. Furthermore, transferring the M. arginini contamination to another cell line renders the newly infected cell line susceptible to peptide binding. Immunolocalization experiments suggest that the peptide is binding to M. arginini adhered to the cell surface. The free synthetic peptide retains its binding in the absence of the phage vehicle and tetramerization of the peptide increases its affinity for the infected cells. Efforts have been made to use this peptide to eliminate Mycoplasma from infected cell lines using ferromagnetic beads coated with the selected peptide. A ten-fold reduction of infection was accomplished with one fractionation via this approach. Our results suggest that this peptide, isolated from an unbiased selection, may be of utility for the detection and reduction of Mycoplasma infection in cultured cells. Furthermore, a general implication of our findings is that phage display methods may be useful for identifying peptides that target a broad array of other biological pathogens in a specific fashion.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...