Volatile arsenic species generated by UV irradiation of aqueous solutions of arsenite in low molecular weight (LMW) carboxylic acid media (formic, acetic, propionic and butyric) were identified using ICP-TOF-MS and GC-MS. Cryogenic trapping-GC-MS reveals that inorganic arsenite can be alkylated to yield AsH3 in the presence of formic acid, trimethylarsine in acetic acid, triethylarsine in propionic acid and tripropylarsine in butyric acid solutions. Mixed ligand arsenic species such as methylarsine, dimethylarsine, dimethylethylarsine and diethylmethylarsine are also formed when a mixture of acids is used. Using 0.05 mg l−1 As(III) as the test solution in 3.1 M acetic acid, a methylation efficiency of approximately 75% was achieved.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
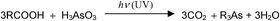

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...