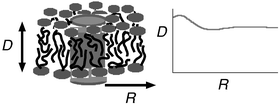
We examined the effect of the insertion of a trans-membrane peptide or protein on the thermodynamic, structural and mechanical characteristics of a lipid bilayer using self-consistent field (SCF) theory. The peptide or protein is modeled as a rigid cylindrical body with a hydrophobic surface and two hydrophilic end caps. We first characterise the properties of the undisturbed bilayer consisting of lipids with a hydrophilic phosphatidylcholine-like head group of nine segments and two identical tails ranging from 8 to 19 alkyl segments. The structural properties are given in terms of thickness of the hydrophobic core d0l and the area a0 per lipid. The mechanical or elastic properties are characterised by the mean bending modulus kc, the saddle splay modulus ![[k with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_006b_0304.gif) and the area compression–expansion modulus of the bilayer ka and its monolayers. Furthermore we calculated the spontaneous curvature Jm0 of the individual monolayer, which can be positive or negative depending on the tail length. Subsequently, we focus on the effect of hydrophobic mismatch between the bilayer and inclusion. The free energy of insertion is parabolic in the mismatch. The minimum is at a small negative mismatch, i.e., when the hydrophobic thickness of the rod is smaller than that of the bilayer. This is attributed to conformational restrictions of the lipid tails close to the rod. This results in a positive curvature of the bilayer adjacent to it, even if the hydrophobic thickness of the rod is larger than that of the bilayer. The bilayer deformation has a wave character which decays exponentially. We show that the decay length of this perturbation is the same as the elastic length (kc(d)2/ka)1/4, provided that for the thickness d of the bilayer d0l is used.
and the area compression–expansion modulus of the bilayer ka and its monolayers. Furthermore we calculated the spontaneous curvature Jm0 of the individual monolayer, which can be positive or negative depending on the tail length. Subsequently, we focus on the effect of hydrophobic mismatch between the bilayer and inclusion. The free energy of insertion is parabolic in the mismatch. The minimum is at a small negative mismatch, i.e., when the hydrophobic thickness of the rod is smaller than that of the bilayer. This is attributed to conformational restrictions of the lipid tails close to the rod. This results in a positive curvature of the bilayer adjacent to it, even if the hydrophobic thickness of the rod is larger than that of the bilayer. The bilayer deformation has a wave character which decays exponentially. We show that the decay length of this perturbation is the same as the elastic length (kc(d)2/ka)1/4, provided that for the thickness d of the bilayer d0l is used.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[k with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_006b_0304.gif) and the area compression–expansion modulus of the bilayer ka and its monolayers. Furthermore we calculated the spontaneous curvature Jm0 of the individual monolayer, which can be positive or negative depending on the tail length. Subsequently, we focus on the effect of hydrophobic mismatch between the bilayer and inclusion. The free energy of insertion is parabolic in the mismatch. The minimum is at a small negative mismatch, i.e., when the hydrophobic thickness of the rod is smaller than that of the bilayer. This is attributed to conformational restrictions of the
and the area compression–expansion modulus of the bilayer ka and its monolayers. Furthermore we calculated the spontaneous curvature Jm0 of the individual monolayer, which can be positive or negative depending on the tail length. Subsequently, we focus on the effect of hydrophobic mismatch between the bilayer and inclusion. The free energy of insertion is parabolic in the mismatch. The minimum is at a small negative mismatch, i.e., when the hydrophobic thickness of the rod is smaller than that of the bilayer. This is attributed to conformational restrictions of the 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...