Two-dimensional (2D) correlation coefficient analyses of heavily overlapped near-infrared spectra
Abstract
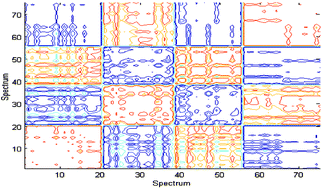
Two-dimensional (2D) correlation coefficient analysis is employed to classify and characterize spectral variations among heavily overlapped near-

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...