Design, synthesis, biological activity and structural analysis of cyclic peptide inhibitors targeting the substrate recruitment site of cyclin-dependent kinase complexes
Abstract
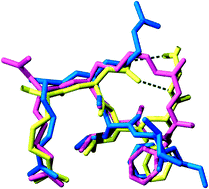
Inhibition of cyclin A- and cyclin E-associated cyclin-dependent kinase-2 (CDK2) activities is an effective way of selective induction of apoptotic cell death via the E2F pathway in tumour cells. The cyclin groove recognition motif (CRM) in the natural CDK-inhibitory (CDKI) tumour suppressor protein p27KIP1 was used as the basis for the design and synthesis of a series of cyclic peptides whose biological activity and structural characterisation by NMR and X-ray crystallography is reported. Whereas linear p27KIP1 sequence peptides were comparatively ineffective, introduction of side chain-to-tail constraints was found to be productive. An optimal macrocyclic ring size for the conformational constraint was determined, mimicking the intramolecular H-bonding system of p27. Molecular dynamics calculations of various macrocycles suggested a close correlation between ring flexibility and biological activity. Truncated inhibitor peptide analogues also confirmed the hypothesis that introduction of a cyclic conformational constraint is favourable in terms of affinity and potency. The structural basis for the potency increase in cyclic versus linear peptides was demonstrated through the determination and interpretation of X-ray crystal structures of complexes between CDK2/cylin A (CDK2A) and a constrained pentapeptide.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...