Photochemistry of the three carboxypyridines in water: a pH dependent reaction
Abstract
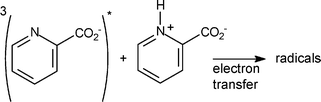
The photochemistry of ortho, meta and para-carboxypyridines (pKa1 = 1.0–2.1 and pKa2 = 4.7–5.3) in aqueous medium was studied by laser-flash photolysis and product studies. At pH < pKa1, hydroxylated compounds are produced with low quantum yields. Within the pH range 4–7, ortho and meta isomers undergo dimerization together with decarboxylation with a quantum yield showing a very sharp maximum around pKa2 (ϕmax = 0.09 and 0.01, respectively) while the para isomer is photostable. End-of-pulse transients assigned to triplet states were detected by laser-flash photolysis at pH < pKa1 and pH > 4. Additionally, the carboxypyridinyl radicals were detected as secondary intermediates at pH < pKa1 and 4 < pH < 7 and the OH-adduct radicals at pH < pKa1. This is in favour of an electron transfer reaction between triplet and starting compound producing a charge transfer species. The radical anion would escape as carboxypyridinyl radical while the radical cation may add water at pH < pKa1 yielding the OH-adduct radical or may undergo decarboxylation at pH > 4. The high quantum yield of phototransformation of the ortho isomer at pH > 4 is due to an easy decarboxylation process. A reaction scheme is proposed accounting for the dependences of ϕ on both the pH and the carboxypyridines concentration. This study points out the distinct pattern of reactivity of carboxypyridines depending on the ionisation state of starting compounds and isomeric substitution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...