Structural identification of europium(iii) adsorption complexes on montmorillonite
Abstract
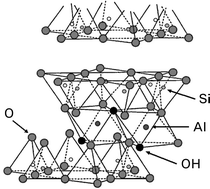
A study of trivalent europium retention onto Na-montmorillonite is presented, combining both macroscopic and microscopic points of view. In order to investigate the metal sorption mechanisms at a molecular level and therefore experimentally identify both clay reactive sites and sorption equilibria, laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) on europium ion loaded montmorillonite have been performed. Moreover, since this clay is an alumino-silicated mineral, we have interpreted our experimental results in terms of interactions between a metal ion and a cation exchange site, and distinct “aluminol” and “silanol” edge sites. Therefore, identical structural investigations have been carried out on both Eu/alumina and Eu/silica systems. These comparisons have allowed us to determine the nature of the europium surface complexes and thus led to an experimental definition of the sorption equilibria involved in the retention process. The obtained lifetime values and the Eu 3d XPS spectra of europium sorbed on the three solids have shown that this metal is sorbed, on the montmorillonite clay, on exchange sites as an outer-sphere complex and onto both “aluminol” and “silanol” edge sites as inner-sphere surface complexes, depending on the pH value and the ionic strength of the suspension.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...