Self-assembled monolayers of diamine molecules and phosphomolybdic acid on an ITO surface
Abstract
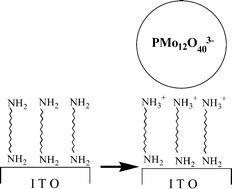
Self-assembled monolayers of 1,12-diaminododecane were prepared on an ITO surface and characterized by cyclic voltammetry, imine formation, secondary ion mass spectroscopy, and Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy (RBS). The surface concentration of 1,12-diaminododecane was measured to be a maximum of 9 × 10−10 mol cm−2 using RBS. Utilizing the surface amine functional group on the self-assembled monolayers of 1,12-diaminododecane, secondary layers of phosphomolybdic acid were prepared and monitored by cyclic voltammetry. The self-assembled monolayers of 1,12-diaminododecane were stable both physically and chemically, and even survived after exposure to air for 4 months

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...