Synthetic analogue approach for the functional domains of copper(ii) bleomycins and its DNA cleavage activity†
Abstract
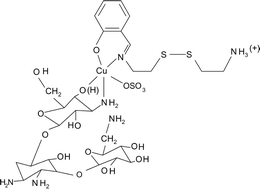
The dicopper(II) complex [Cu2(R′SSR)2(SO4)2] (1), where R′SSR is a Schiff base, has been prepared from the reaction of CuSO4·5H2O with the Schiff base N,N′-1,1′-dithiobis(ethylenesalicylaldimine) (H2RSSR) and structurally characterized by X-ray crystallography. The crystal structure of 1 shows two {Cu(R′SSR)}2+ units linked by two sulfate ligands each showing a η3,μ2-binding mode. The Cu⋯Cu distance is 4.562(2) Å with each copper having a square pyramidal (4 + 1) CuNO4 coordination geometry. The monoanionic Schiff base R′SSR has a pendant cationic amine –SCH2CH2NH3+ group which is presumably formed from the hydrolysis of one imine bond of H2RSSR. Complex 1 models the N- and C-terminus domains of bleomycins. The metal centers in 1 are essentially magnetically non-interacting giving a −2J value of 3 cm−1 with the singlet as the ground state. Using complex 1 as a precursor, ternary copper(II) complexes [Cu(R′SSR)B(SO4)] (2–4) are prepared, characterized and their DNA binding and cleavage properties studied (B: kanamycin A, 2; 2,2′-bipyridine, 3; 1,10-phenanthroline, 4). IR spectral data suggest a square pyramidal (4 + 1) geometry for the one-electron paramagnetic ternary complexes with the sulfate bound to copper. The complexes are non-conducting in DMF but show conductivity in aqueous medium due to dissociation of the sulfate ligand. They bind to calf thymus DNA in the minor groove giving the relative order: 4 > 2 > 1 ∼ 3 (Kapp = 5.4 × 105 M−1 for 4). The precursor complex 1 does not show any apparent chemical nuclease activity when treated with supercoiled (SC) DNA in the presence of 3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA). The kanamycin A and phen adducts as such or generated under in situ reaction conditions using 1 and the ligand display efficient chemical nuclease activity in the presence of MPA, while the bpy species shows poor cleavage activity. The ternary kanamycin A complex presents the first synthetic model for three functional domains of bleomycins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...