Kinetics and mechanism of the ferroxime(ii)-catalysed biomimetic oxidation of 2-aminophenol by dioxygen. A functional phenoxazinone synthase model†
Abstract
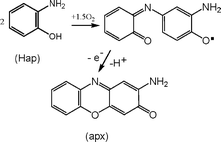
[Fe(Hdmg)2(MeIm)2] (1), referred to as ferroxime(II), is the precursor of a selective catalyst for the oxidative dehydrogenation of 2-aminophenol (Hap) to 2-amino-3H-phenoxazine-3-one (apx) by dioxygen under ambient conditions. The superoxoferroxime(III) species has been detected by ES-MS, and a 4-substituted 2-aminophenoxyl free radical by the ESR technique. The kinetics of the reaction was followed spectrophotometrically and by monitoring dioxygen uptake at constant pressure. According to the proposed mechanism, solvolysis of 1 is followed by O2 binding to afford a superoxoferroxime, which abstracts an H-atom from Hap in the rate-determining step via an H-bonded intermediate, generating the free radical. This is supported by the observed primary deuterium kinetic isotope effect of 2.63. The system studied is a functional phenoxazinone synthase model.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...