Porphyrin–aminoquinoline conjugates as telomerase inhibitors
Abstract
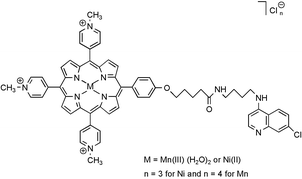
A series of metalloporphyrins was prepared in order to target the G-quadruplex structure of telomeric DNA for the design of antitelomerase compounds. The initial cationic tetramethylpyridiniumyl porphyrin was modified by the replacement of one or two methylpyridiniumyl groups by one or two 4-aminoquinoline moieties, at the meso position, in order to increase the cell penetration and the quadruplex affinity. The porphyrins were either metallated by manganese or by nickel. The degradation of quadruplex DNA was assayed in vitro with the manganese redox-active derivatives. All porphyrins complexes were capable of inhibiting the telomerase enzyme with IC50 values in the micromolar range (TRAP assay).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...