Metal ion-activated molecular receptors for aromatic anions with receptor cavities formed from 1- or 2-naphthyloxy moieties appended to cyclen
Abstract
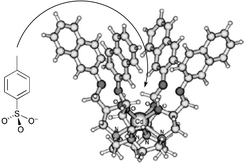
Studies of two newly synthesised, isomeric metal ion-activated molecular receptors, [Cd(1,4,7,10-tetrakis{(S)-(−)-2-hydroxy-3-(1′-naphthyloxy)propyl}-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane)](ClO4)2·H2O and [Cd(1,4,7,10-tetrakis{(S)-(−)-2-hydroxy-3-(2′-naphthyloxy)propyl}-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane)](ClO4)2, show that both act as molecular receptors for the p-toluenesulfonate anion. The binding cavity depths for the two receptors were calculated from ab initio molecular modelling to be 4.81 and 7.27 Å, respectively. Despite the smaller cavity depth for the first receptor, it forms the more stable inclusion complexes, as assessed by the relative magnitude of the decrease in electrical conductivity and

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...