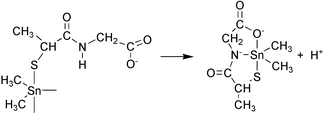
The coordination properties of the simple dipeptide L-alanyl-glycine (Ala-Gly) towards dimethyltin(IV) cation have been compared with its mercapto analogue N-(2-mercaptopropionyl)glycine (MPGly), using potentiometric, 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopic methods. The replacement of the terminal amino group of Ala-Gly by a thiol group (MPGly) induces fundamental changes in the coordination processes and in the speciation of metal complexes, though the composition of the species formed is identical. The considerably higher stability of the MPGly complexes is due to the outstanding affinity of dimethyltin(IV) cation toward sulfur donor atoms. In the MLH and ML complexes, formed in the acidic pH range, monodentate carboxylate and thiolate coordination has been observed for Ala-Gly and MPGly, respectively. Therefore, different donor groups in the case of the two ligands assist the metal promoted deprotonation of amide nitrogen. Our data provide the first example, that thiolate can act as an anchoring group in the diorganotin(IV) induced amide deprotonation.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...