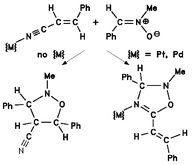
[2 + 3] Cycloaddition of N-methyl-C-phenylnitrone to transition metal coordinated (E)-cinnamonitrile occurs exclusively at the nitrile C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N bond, leading to Δ4-1,2,4-oxadiazoline complexes, from which the heterocyclic ligand can be released and isolated in high yield. In contrast, the reaction of the nitrone with free cinnamonitrile involves the C
N bond, leading to Δ4-1,2,4-oxadiazoline complexes, from which the heterocyclic ligand can be released and isolated in high yield. In contrast, the reaction of the nitrone with free cinnamonitrile involves the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond only, yielding a diastereomeric mixture of isoxazolidine-4-carbonitriles. Microwave irradiation enhances the reaction rates of both transformations considerably, without changing their regioselectivity with respect to the thermal reactions. The two nitrile ligands in complexes of the type [MCl2(cinnamonitrile)2]
(M = Pt or Pd) are significantly different in reactivity. Thus, short-time microwave irradiation allows for the selective synthesis of the mono-cycloaddition product [PtCl2(cinnamonitrile)(oxadiazoline)], even in the presence of an excess of nitrone. Using longer irratiation times, this complex can be further transformed into the bis-cycloaddition product [PtCl2(oxadiazoline)2]. The latter compound is also produced when thermal heating is applied, however, the formation of the mono-cycloaddition product fails to be selective under thermal conditions.
C bond only, yielding a diastereomeric mixture of isoxazolidine-4-carbonitriles. Microwave irradiation enhances the reaction rates of both transformations considerably, without changing their regioselectivity with respect to the thermal reactions. The two nitrile ligands in complexes of the type [MCl2(cinnamonitrile)2]
(M = Pt or Pd) are significantly different in reactivity. Thus, short-time microwave irradiation allows for the selective synthesis of the mono-cycloaddition product [PtCl2(cinnamonitrile)(oxadiazoline)], even in the presence of an excess of nitrone. Using longer irratiation times, this complex can be further transformed into the bis-cycloaddition product [PtCl2(oxadiazoline)2]. The latter compound is also produced when thermal heating is applied, however, the formation of the mono-cycloaddition product fails to be selective under thermal conditions.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N bond, leading to Δ4-1,2,4-oxadiazoline complexes, from which the heterocyclic
N bond, leading to Δ4-1,2,4-oxadiazoline complexes, from which the heterocyclic ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond only, yielding a diastereomeric mixture of isoxazolidine-4-carbonitriles. Microwave irradiation enhances the reaction rates of both transformations considerably, without changing their regioselectivity with respect to the thermal reactions. The two
C bond only, yielding a diastereomeric mixture of isoxazolidine-4-carbonitriles. Microwave irradiation enhances the reaction rates of both transformations considerably, without changing their regioselectivity with respect to the thermal reactions. The two 

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...