New insights into the solution equilibrium of molybdenum(vi)–hydroxamate systems: 1H and 17O NMR spectroscopic study of Mo(vi)–desferrioxamine B and Mo(vi)–monohydroxamic acid systems
Abstract
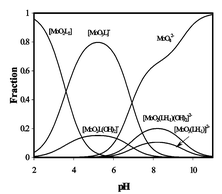
To complement our previous pH-potentiometric and spectrophotometric investigations, in the present work 17O NMR studies on Mo(VI)–desferrioxamine B (DFB) and Mo(VI)–acetohydroxamic acid (Aha) systems, and 1H NMR on Mo(VI)–Aha, Mo(VI)–benzohydroxamic acid (Bha) and –N-methylacetohydroxamic acid (MeAha) have been performed. Complete equilibrium models for all the studied systems are presented in this paper. Formation of a hydrogen bond could be suggested between the hydroxamate-NH of the coordinated primary monohydroxamic acids and oxo ligands of molybdenum under acidic conditions and, at ca. neutral pH, deprotonation of that NH was found. This is the first time that this process in a Mo(VI)–hydroxamic acid system has been detected. The hydroximato chelate formed in this manner is unusually stable, and able to compete with hydrolytic processes up to basic pH, which results in the surprising fact that the interaction between Mo(VI) and the small primary molecules, Aha and Bha exists up to much higher pH than between Mo(VI) and the known powerful tris-chelator natural compound, DFB.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...