The reaction enthalpies for the photoreduction of n,π*-excited states (acetone, benzophenone, 2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-2-ene, and a 2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene derivative) by model hydrogen donors (methanol and dimethylamine) were calculated on the basis of a critically evaluated data set of bond dissociation energies for donors and reduced acceptors. These were compared with the observed photoreactivity, which can be assessed through quenching rate constants of the excited states by hydrogen donors. The intriguing observation of a preferential attack at electrophilic hydrogen atoms, i.e., N–H or O–H, by n,π*-excited azoalkanes is rationalised on the basis of the calculated thermochemical data, differences in electrophilicity, and varying contributions of antibonding character in the transition state. Singlet-excited azoalkanes act as nucleophilic species, while excited ketones display an electrophilic reactivity.
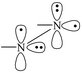
This is in line with the pictorial description of the electron distribution in these excited states.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...