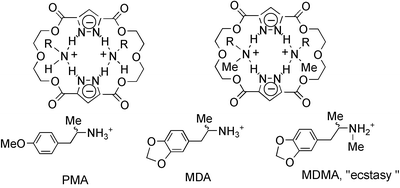
The equilibrium stability constants (Ks) of ammonium pyrazolate complexes [L2−]2RN(R′)H2+ (3, R′
= H and 4, R′
= Me) formed from a macrocyclic disodium dipyrazolate salt 2[L2−] 2Na+ and ammonium salts (RNH3+X− or RN(Me)H2+X−) of psychotropic drugs and neurotransmitter catecholamines have been evaluated by electrochemical methods in DMSO solution. The resulting Ks values demonstrate that, except for (±)-amphetamine, the complexes formed by lipophilic primary [mescaline, (+)-amphetamine, (±)-p-methoxyamphetamine (PMA), (±)-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA)] and secondary [(±)-methamphetamine,
(+)-methamphetamine and (±)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA ‘ecstasy’)] phenethylamines are more stable than those formed from hydrophilic ones (dopamine and norepinephrine). A 1H and 13C NMR study on the formation of complexes of structure 3 and 4 formed from primary [mescaline, (+)-amphetamine] and secondary [(+)-methamphetamine] ammonium salts is given.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...