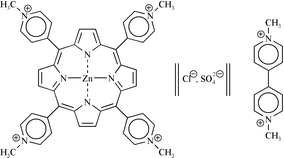
Quenching of the singlet and triplet excited states of Zn(II)
meso-tetrakis(N-methylpyridinium-4-yl)porphyrin (ZnTMPyP4+) by methyl viologen dichloride (MvCl2) in aqueous solutions was studied using steady state fluorescence and laser flash photolysis techniques. External and inner salts added to the solution affect the photophysical properties of the ground and excited states of this ionic zinc porphyrin. The non-covalent association complex between zinc porphyrin and methyl viologen ion pairs can explain the electronic absorption spectral changes, which are enhanced in the presence of sodium chloride. The singlet and triplet excited states quenching experiments, at high quencher concentrations, show that the dynamic quenching is improved in the presence of sodium chloride and sodium sulfate, respectively. The photoinduced electron transfer (PET) process between zinc porphyrin triplet and methyl viologen, in the presence of sodium chloride, increases the triplet quantum yield. The efficiency of the corresponding ion pair radical production (from PET) is affected by the presence of salts being smaller for sodium chloride than for sodium sulfate. Good Arrhenius plots were obtained from the triplet decay quenching rate constant and radical ion formation at three different methyl viologen concentrations. The apparent activation energy (1.3–8.6 kcal mol−1) increases with the quencher concentration until the diffusion activation energy in water is reached and is greater than the diffusion activation energy in ethylene glycol. The electron transfer process associated with the quenching reaction is analysed in terms of the contributions of free ions or ion pairs.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...