Reaction of silylalkylmono- and silylalkyldi-amines with carbon dioxide: evidence of formation of inter- and intra-molecular ammonium carbamates and their conversion into organic carbamates of industrial interest under carbon dioxide catalysis
Abstract
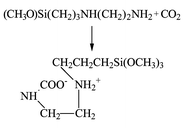
The reactivity of industrially relevant silylalkylamines towards CO2 and dialkyl/arylcarbonates is discussed. The kinetics of uptake of carbon dioxide at various temperatures shows that at 295 K, silylalkylmonoamines react with carbon dioxide in a 2∶1 molar ratio, affording classic intermolecular ammonium carbamates of formula RNHCOO−+NH3R, while at 273 K, dimeric carbammic acids, (RNHCOOH)2, are formed. Conversely, silylalkyldiamines react at 297 K with carbon dioxide to afford zwitterionic intramolecular six-membered cyclic ammonium carbamates of formula RNH2+CH2CH2NHCOO−, a unique example of CO2 uptake by an amine with a 1∶1 molar ratio. Such systems may have a potential application in CO2 separation. The catalytic role of carbon dioxide in the carbamation of the above mentioned amines by reaction with organic carbonates is described.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...