Synthesis of dimethyl carbonate using CO2 and methanol: enhancing the conversion by controlling the phase behavior
Abstract
The critical parameters and phase behavior of the multi-component system CO2-CH3OH–CH3I–H2O–CH3OC(O)OCH3 (dimethyl carbonate, DMC) were determined. The concentrations of the components were selected in such a way that they simulated the compositions of the reaction system at different conversions for synthesizing DMC using CO2 and methanol in a batch reactor. The critical density of the reaction system decreases with the conversion of methanol. The critical temperature and critical pressure of the reaction system increase with the conversion. Based on the determined critical parameters and phase behavior, DMC synthesis using CO2 and methanol was run at various pressures that corresponded to conditions in the two-phase region, the critical region as well as the single-phase supercritical region. The original ratios of the reactants CO2∶CH3OH were 8∶2 and 7∶3, and the corresponding reaction temperatures were 353.2 and 393.2 K, respectively, which were slightly higher than the critical temperatures of the reaction systems. The results indicate that the phase behavior affects the equilibrium conversion of methanol significantly and the conversion reaches a maximum in the critical regions of the reaction system. At 353.2 K, the equilibrium conversion in the critical region is about 7%, and can be about three times as large as those in other phase regions. At 393.15 K, the equilibrium conversion in the critical region is also much higher and can be twice as large as those in other phase regions.
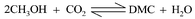

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...